Introduction
Telemedicine involves using communication and electronic information technologies to provide and support healthcare when participants are separated by distance. In particular, it encompasses video chat and phone appointments in delivering medical care remotely. Telemedicine is beneficial since it simplifies access to specialists. In this respect, telemedicine’s impacts on patient-centered care include improved patient-provider relationships, increased patient data access, and affordability.
Improved Relationship Between Patients and Health Care Practitioners
Telemedicine has played a significant role in improving the connection between patients and medics. Telemedicine guarantees the maintenance of provider-patient relationships, ensuring continuity of care remotely (Andreadis et al. 2023, p. S85). In this respect, patient-centered care encourages patients to take an active role in their care. Hence, they require minimal attention from providers. However, healthcare practitioners require follow-up to ensure patients are on the right track of maintaining their health. Telemedicine provides an opportunity for patients and providers to have regular conversations. The discussions ensure that the parties build a strong relationship guaranteeing better patient health. A cohesive provider-patient relationship enhances the self-confidence in self-management of a patient. Therefore, telemedicine improves the patient-provider relationship, which is critical in enhancing adherence to patient-centered care.
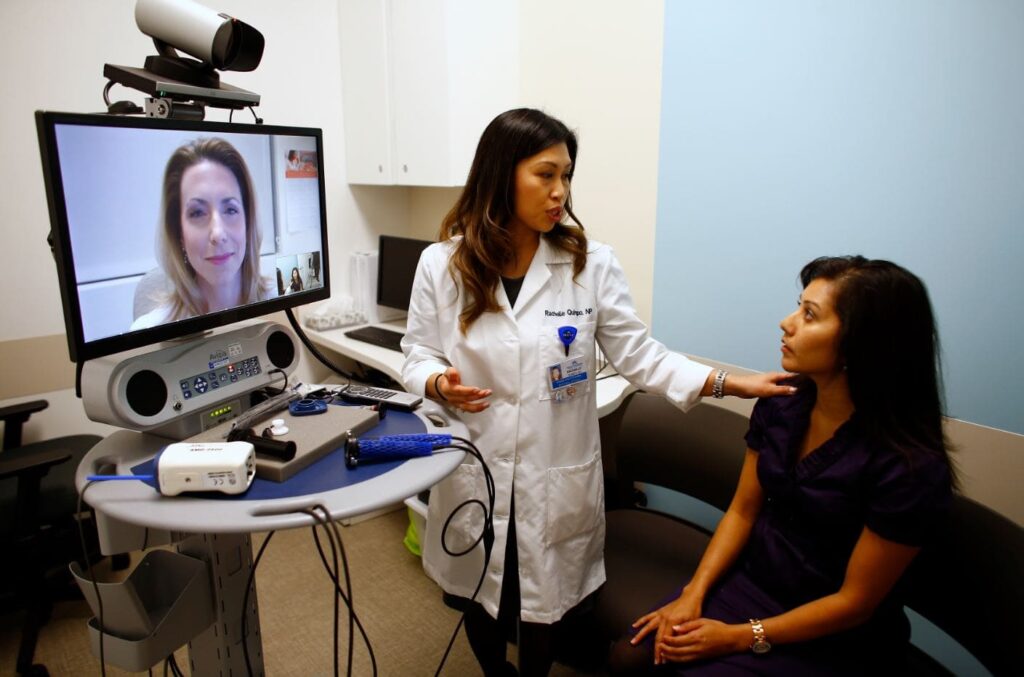
Increased Access to Information
Telemedicine has impacted patient-centered care by increasing access to patient information. Telemedicine has contributed to using user-friendly devices to gather data and vitals that promote remote assessment (Barbosa et al. 2021, p. 467). In this case, it has enabled electronic health records to facilitate information sharing among various providers. Patients’ health data is significant to providers in understanding their progress, improving diagnosis, and developing new treatments. In this context, telemedicine ensures that healthcare systems create a holistic view of patients’ conditions and develop personalized treatment plans. In patient-centered care, telemedicine is significant since patients can access help from providers when they need it through the Internet. Providers collect critical information during the discussions to track a patient’s progress. Proper data storage ensures that if the patient requires medical attention, there is adequate information to make essential decisions. For instance, hub-and-spoke telestroke systems support real-time data and communication sharing between multiple community emergency departments and single tertiary care centers (Barbosa et al. 2021, p. 468). This approach ensures healthcare centers aid patients’ treatment management, especially those in remote areas. Therefore, telemedicine in patient-centered care has promoted data sharing, which makes it easy to access patients’ information for enhanced treatment.
Increased Affordability
Telemedicine has ensured the affordability of healthcare in patient-centered care, increasing people’s quality of life. For instance, telemedicine decreases costs by eliminating the necessity to travel to get particular clinical expertise (Alanazi, Al Hader & Hader 2022, p. 1). In particular, it reduces out-of-pocket payments, lowering healthcare expenses. The cost reduction guarantees healthcare services’ affordability, especially for low-income families. Cost decrease ensures patients involved in patient-centered care are more responsible and adhere to treatment plans due to affordability, ensuring most patients get better outcomes.
Conclusion
Telemedicine has impacted patient-centered care by enhancing affordability, promoting data sharing, and improving patient-provider relationships. Telemedicine ensures that patients make regular inquiries and get quick responses to maintain a provider-patient relationship. Besides, it encourages data storage and sharing, ensuring providers make informed decisions. In turn, telemedicine reduces costs in patient-centered care by cutting out-of-pocket payments, which provides the affordability of healthcare services.
Reference List
Alanazi, AT, Al Hader, B & Hader, B 2022, ‘Telemedicine patient satisfaction and cost: A comparative study in the COVID-19 Era’, Cureus, vol. 14, no. 10, pp. 1-6, viewed 8 July -2023, DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofab661.
Andreadis, K, Muellers, K, Ancker, JS, Horowitz, C, Kaushal, R & Lin, JJ 2023, ‘Telemedicine impact on the patient–provider relationship in primary care during the COVID-19 pandemic’, Medical Care, vol. 61, no. 1, pp. S83- S88, viewed 8 July 2023, DOI: 10.1097%2FMLR.0000000000001808.
Barbosa, W, Zhou, K, Waddell, E, Myers, T & Dorsey, ER 2021, ‘Improving access to care: Telemedicine across medical domains’, Annual Review of Public Health, vol. 42, pp. 463-481, viewed 8 July 2023, DOI: 10.1146/annurev-publhealth-090519-093711.


