Rules that guide academic writing are specific to each paper format. However, some rules apply to all styles – APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, and Harvard. Basically, one of these rules is the inclusion of a table of contents (TOC) in an academic text, particularly long ones, like theses, dissertations, and research papers. Before starting a TOC, students or researchers should observe some practices regardless of different paper formats. Moreover, the process includes putting a particular TOC on a new page after the title page, numbering the first-level and corresponding second-level headings, and indicating the page number of each entry. Hence, scholars need to learn how to write a good table of contents in APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, and Harvard styles. Additionally, they may explore guides on how to write a critique to improve their organizational skills.
General Guidelines
When organizing academic texts, such as theses, dissertations, and other research papers, students observe academic writing rules as applicable. Generally, the different paper formats – APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, and Harvard – have specific standards that students must follow strictly. In this case, one of the rules is the inclusion of a table of contents (TOC) in the document. By definition, a TOC is a roadmap that scholars provide in their composition, outlining each portion of a paper. In other words, it enables readers to locate specific information in documents or revisit favorite parts within completed texts. To make a good table of contents, writers ensure it is accurate, consistently formatted, clearly organized with proper headings and subheadings, and includes correct page numbers for all major sections and subsections. Moreover, this part of academic papers provides readers with a preview of the document’s text.

What Is a Table of Contents and Its Purpose
According to its definition, a table of contents (TOC) is a structured list that can be found at the beginning of books, reports, or other documents and provides key details on their chapters, sections, and major topics, along with their corresponding page numbers. The main purpose of writing a table of contents is to provide a clear and organized overview of a document’s text and help readers to understand its organization and flow of a material, making it easy to navigate (Heard, 2022). In this case, writers place their table of contents immediately after the title page and acknowledgments but before the main body of an entire work. Moreover, in lengthy or complex compositions, such as essays, research papers, theses, or dissertations, scholars often need to reference only specific information without reading them (Lewis et al., 2021). To achieve this purpose, they review a TOC page of a particular work under analysis and efficiently access the parts they need. Overall, a well-designed table of contents significantly improves the reader’s experience by providing a valid roadmap to a particular document’s text (Stadtlander, 2022). Besides, a dissertation table of contents should include all major sections, such as the introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, references, and appendices, along with their respective subsections and corresponding page numbers. In turn, here is an example template for writing a dissertation table of contents:
Difference Between a Table of Contents and an Outline
In essence, a TOC is a description of first-level headings (topics) and second-level headings (subtopics) within the paper’s body. For a longer document, writers may also include third-level titles to make the text good to read. To create a table of contents in Word, writers use the “References” tab to select “Table of Contents” and choose a style, ensuring that their document’s headings are formatted with the appropriate heading styles. Ideally, the length of papers determines the depth that authors go into detailing their writing in TOCs. For example, popular table of contents designs include hierarchical lists with indented subsections, dot leaders connecting titles to page numbers, and clear, consistent formatting with bold or italicized headings to distinguish different levels (Fitzpatrick, 2021). Basically, this feature means that shorter texts may not require third-level headings. In contrast, an essay outline is a summary of the paper’s main ideas with a hierarchical or logical structuring of the text. Unlike a TOC that only lists headings and subheadings, outlines capture these headings and then describe a written composition briefly under each one. As such, an outline provides a more in-depth summary of essay papers compared to a TOC.
Criteria
| Criteria | Rule |
|---|---|
| Font and Style | Use a readable font (e.g., Times New Roman, Arial, Calibri) and a consistent font size (12-point). Use bold or italics sparingly for section titles. |
| Alignment and Indentation | Left-align main headings. Indent subsections to reflect hierarchy (e.g., 0.5 inches for each level). |
| Spacing | Single or 1.5 line spacing within entries. Double space between major sections. |
| Capitalization | Use title case (capitalize major words) for section titles. Ensure consistent capitalization style. |
| Page Numbers | Align page numbers to the right margin. Use dot leaders to connect section titles to page numbers. |
| Headings and Subheadings | Distinguish different levels of headings (e.g., main headings in bold, subheadings in regular font). Use numbering for chapters and sections (e.g., 1. Introduction, 1.1 Background). |
| Consistency | Apply formatting rules consistently throughout an entire TOC. Ensure formatting matches the rest of the document. |
| Lists of Figures and Tables | Follow same formatting rules as a main TOC. Place these lists immediately after a TOC page. |
| Margins | Use standard document margins (e.g., 1-inch margins on all sides). Ensure it fits within margins without overcrowding. |
| Templates and Styles | Use predefined styles or templates to ensure consistency. Adjust styles as necessary for specific requirements. |
Importance
- Easing a Document Navigation: Allows readers to quickly locate specific sections or chapters without having to search through an entire work.
- Providing an Overview: Offers a clear and structured outline of a paper’s text, helping readers understand the scope and organization at first glance.
- Improving Readability: Breaks down a written document into manageable sections, helping readers to follow and comprehend its content.
- Promoting Easy Reference: Enables readers to reference specific parts of a document easily, which is particularly useful for lengthy works, like dissertations, reports, or manuals.
- Making a Professional Presentation: Adds a level of professionalism and polish to a completed work, demonstrating attention to detail and careful organization.
- Aiding in Document Structuring: Helps writers to organize their thoughts and structure their papers logically, ensuring a coherent flow of information.
- Saving Time: Saves readers time by providing direct access to the sections they are interested in, improving overall efficiency.
- Supporting Academic and Technical Standards: Meets the requirements of academic and technical writing standards, which often mandate a TOC for comprehensive documents.
- Facilitating Review and Editing: Assists reviewers and editors in navigating a completed paper quickly, making the review and editing process more efficient.
- Enhancing Accessibility: Makes an entire document more accessible to a wider audience, including those who may need to find information quickly for research or reference purposes.
General Format
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Title Page | The title of an entire document with an author, institution, and date. |
| Abstract | A brief summary of a document’s content. |
| Acknowledgments | Section to thank those who helped in the creation of this document. |
| Table of Contents | A list including all sections and subsections with page numbers. |
| List of Figures or Illustrations | A list covering all figures in this document with page numbers. |
| List of Tables | A list presenting all tables in this document with page numbers. |
| List of Abbreviations | Definitions of abbreviations used in this document. |
| List of Symbols | Descriptions of symbols used in this document. |
| Chapters and Sections | The paper’s main content organized as chapters and sections. |
| Introduction | Overview, research problem, objectives, and significance. |
| Literature Review | Summary of existing research related to a study topic. |
| Methodology | Methods used for research, including data collection and analysis. |
| Results | Presentation and analysis of research findings. |
| Discussion | Interpretation of results, implications, and comparison with existing literature. |
| Conclusion and Recommendations | Summary of findings, conclusions drawn, and suggestions for future research. |
| Reference List | A list acknowledging all sources cited in a finished document and according to APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, Harvard, or other referencing formats. |
| Appendices | Additional materials, such as surveys, detailed data, and supplementary information. |
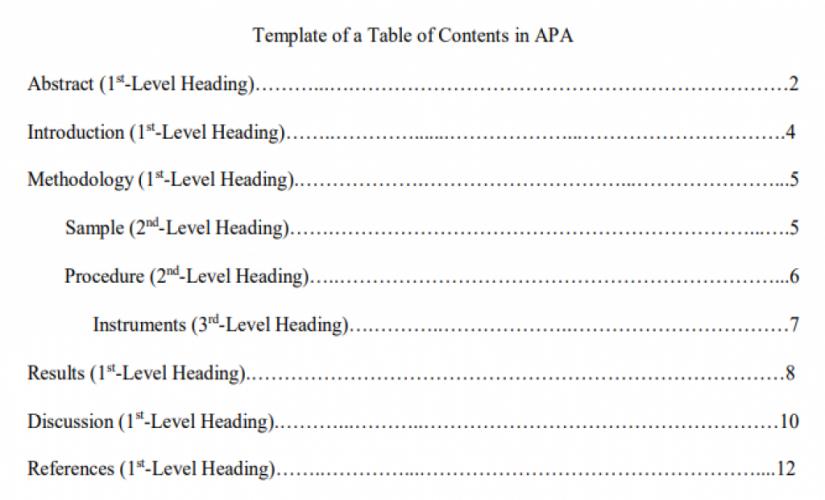
How to Write a Table of Contents in APA
When writing a TOC in the APA format, writers should capture all the headings in the paper – first-level, second-level, and even third-level. Besides this information, they should also include an abstract, references, and appendices. The correct way to format a table of contents is to list all main sections and subsections in a logical order, use clear and consistent headings, indent subsections, align page numbers to the right with dot leaders connecting the titles to them, and ensure it matches the overall document style and layout (Lang, 2017). Notably, while a TOC in the APA style has an abstract, this section is not necessary for the other formats, like MLA, Chicago/Turabian, and Harvard. Hence, an example of a TOC written in APA format is indicated below:
How to Write a Table of Contents in MLA
Unlike papers written in the APA style, MLA papers do not require a table of contents unless they are long enough. In this case, documents, like theses, dissertations, and books organized in the MLA format should have a TOC. For example, a table of contents in a book is a list of the chapters and major sections, along with their corresponding page numbers, providing an organized overview of its structure and text (Silvia, 2015). Even where a TOC is necessary, there is no specific method that a writer should use when writing it, and its structure is left to the writer’s discretion. To write a table of contents, writers list the main sections and subsections of their documents in the order they appear, using consistent formatting and including corresponding page numbers for each entry. However, when they have to include a TOC in their compositions, the information they capture should be much more than what would appear in the APA paper. Hence, an example of writing a TOC in MLA format is:

To create a good table of contents, writers ensure it is well-organized, accurately lists all sections and subsections with corresponding page numbers, and is formatted consistently for clarity and ease of navigation. In the case of writing a research paper, an example of an MLA TOC should be:

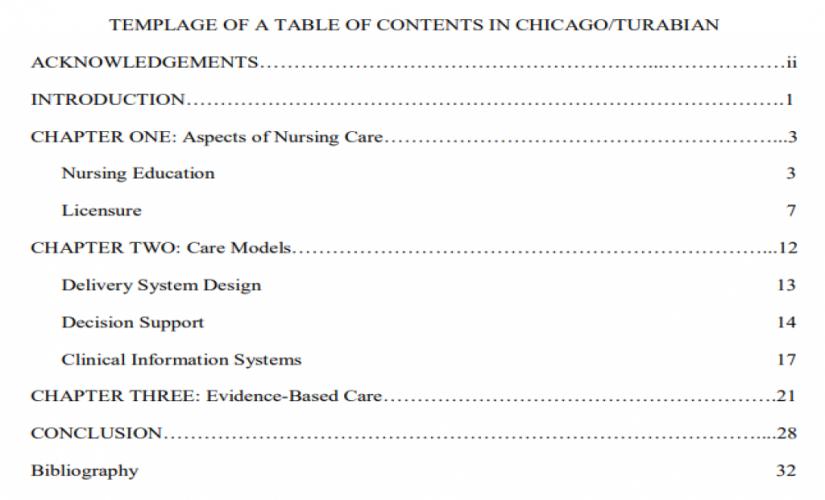
How to Write a Table of Contents in Chicago/Turabian
Like the MLA style, a Chicago/Turabian paper does not require writing a table of contents unless it is long enough. When a TOC is necessary, writers should capitalize on major headings. In this case, authors do not need to add a row of periods (. . . . . . . .) between the heading entry and the page number. Writers should use a table of contents format that lists all main sections and subsections in proper order, with clear headings, correct indentation for hierarchy, dot leaders connecting titles to right-aligned page numbers, and consistent formatting throughout (Stadtlander, 2022). Then, the arrangement of the text should start with the first-level heading, then the second-level heading, and, finally, the third-level title, just like in the APA paper. In turn, all the information that precedes the introduction part should have lowercase Roman numerals. Besides, the row of periods is only used for major headings. Therefore, an example of writing a TOC in Chicago/Turabian format is:
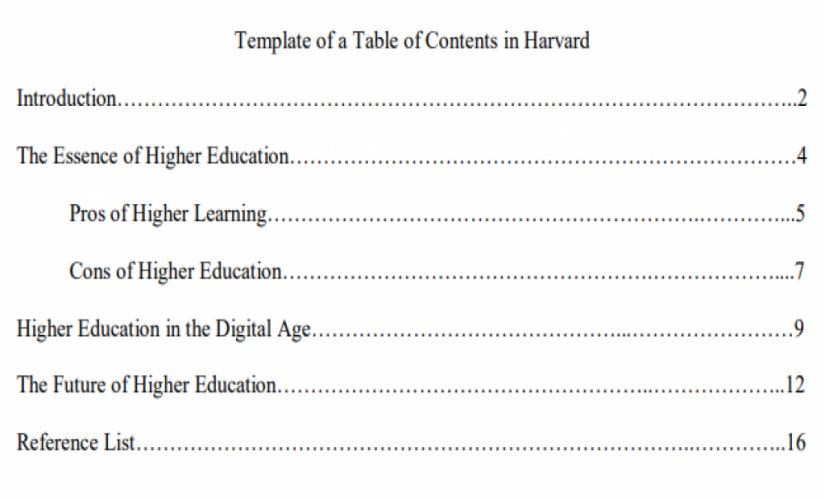
How to Write a Table of Contents in Harvard
Like in the other formats, writing a table of contents in the Harvard style is captured by having the title “Table of Contents” at the center of the page, in the first line. Basically, it comes after the title page and captures all the sections and subsections of Harvard papers. In other words, writers must indicate first-level headings in a numbered list. For example, to create a good table of contents, writers list the document’s main sections and subsections in the order they appear, apply consistent formatting, and include corresponding page numbers for each heading (Heard, 2022). Further on, scholars should align titles to the left side and capitalize them. In turn, if there is a need to show second-level headings, authors should list them under corresponding first-level headings by using bullet points. However, it is essential for students not to disrupt the numbering of first-level headings. Besides, writers should align second-level headings to the left side and indent them by half an inch and capitalize on a choosen piece. As a result, an example of writing a TOC in Harvard format should appear as below:
Common Mistakes
- Inconsistent Formatting: Using different fonts, sizes, or styles within a single TOC.
- Incorrect Page Numbers: Page numbers in a TOC do not match actual text pages.
- Missing Sections: Omitting important sections or subsections from a TOC.
- Overly Detailed Entries: Including too much detail makes a particular TOC hard to read.
- Lack of Subheadings: Not breaking down major sections into subheadings for clarity.
- Unclear Section Titles: Using vague or unclear titles does not reflect a completed text accurately.
- Improper Indentation: Incorrectly indenting headings and subheadings makes their hierarchy unclear.
- Inconsistent Capitalization: Using different capitalization styles for headings and subheadings.
- Failure to Update: Not updating a completed TOC after making changes to some sections of a final work.
- Missing List of Figures/Tables: Not including lists for figures and tables if they are present in a research paper.
- Ignoring Styles/Templates: Not using document styles or templates for doing a good TOC leads to inconsistency.
- Overly Long Titles: Including overly long section titles makes an entire TOC difficult to read.
Summing Up
Any TOC is an essential component of any academic paper, particularly for long documents, like theses, dissertations, and research papers. When students are writing a TOC, they should be careful to follow the applicable format’s rules and standards. Regardless of the format, writers should master the following tips when doing a TOC page:
- Write a TOC on a new page after the title page.
- Indicate first-level headings of the document in a numbered list.
- Indicate second-level headings under the corresponding first-level heading.
- If applicable, indicate third-level headings under the corresponding second-level heading.
- Write a specific page number for each heading.
- Put the provided content in a two-column table.
- Title the page with “Table of Contents.”
References
Fitzpatrick, R. (2021). Write useful books: A modern approach to designing and refining recommendable nonfiction. Useful Books Ltd.
Heard, S. B. (2022). The scientist’s guide to writing: How to write more easily and effectively throughout your scientific career. Princeton University Press.
Lang, T. A. (2017). Writing a better research article. Journal of Public Health and Emergency, 1, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.21037/jphe.2017.11.06
Lewis, K. B., Graham, I. D., Boland, L., & Stacey, D. (2021). Writing a compelling integrated discussion: A guide for integrated discussions in article-based theses and dissertations. International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship, 18(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1515/ijnes-2020-0057
Silvia, P. J. (2015). Write it up: Practical strategies for writing and publishing journal articles. American Psychological Association.
Stadtlander, L. (2022). Editorial: Rewriting a social science dissertation into a journal article and getting it published. Journal of Social, Behavioral, and Health Sciences, 16(1), 94–102. https://doi.org/10.5590/jsbhs.2022.16.1.07


